The Importance of Solar Battery

Solar power generation is highly dependent on light conditions. When there is plenty of sunlight during the day, there is abundant electricity. However, once night falls or it encounters rainy and cloudy weather, the power generation capacity will drop significantly or even drop to zero, making it difficult for solar power generation to meet the continuous and stable electricity demand alone.
At this time, solar batteries take on the important task of being “power regulators”. They store electrical energy when there is excessive solar power generation and release electrical energy when the power generation is insufficient or there is no power generation at all. In this way, they effectively fill the gap between power supply and demand and ensure the continuity and stability of power supply.
The Working Principle of a Solar Battery
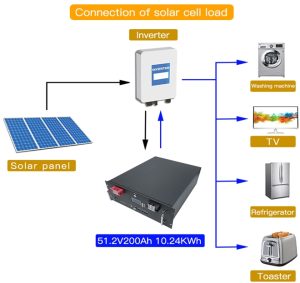

The solar battery system mainly consists of :
- solar panel
- controller (not drawn on the left picture)
- storage battery
- inverter
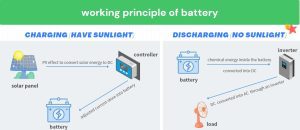
- Charging Process: Under light conditions, solar panels convert solar light energy into DC through the photovoltaic effect. This electrical energy first passes through the controller. The function of the controller is to adjust and control the input electrical energy, including limiting the charging current and voltage to prevent the solar battery from over – charging and ensuring the safety and stability of the charging process. The electrical energy adjusted by the controller is then delivered to the solar battery with appropriate parameters, and the solar battery converts the electrical energy into chemical energy for storage.
- Discharging Process: When the solar panels can’t generate enough electrical energy, such as at night or on a rainy and cloudy day, the storage battery starts to discharge under the monitoring of the battery management system. The chemical energy inside the battery is converted into DC through a chemical reaction. The output DC is then converted into AC through an inverter to meet the AC power requirements of various household, commercial and industrial electrical equipment, thus realizing stable power supply.

Common Types of Solar Batteries
Lead – acid Battery
(1) Principle:
It mainly realizes charging and discharging by means of the chemical reactions between the positive and negative electrode materials and the electrolyte.
- During charging, an external power source applies a certain voltage, causing lead dioxide on the positive electrode and lead on the negative electrode to react with sulfuric acid in the electrolyte respectively, generating lead sulfate and water.
- During discharging, lead sulfate on the negative electrode gains electrons and is reduced to lead. The electrons flow to the positive electrode through the external circuit. Meanwhile, lead sulfate on the positive electrode loses electrons and is oxidized to lead dioxide. The directional movement of electrons generates an electric current.
(2) Advantages:
- It is inexpensive and the technology is mature.
(3) Disadvantages:
- It has a relatively low energy density.
- It is large in size and heavy in weight.
- Its cycle life is relatively short. Generally, it is only about two years (the number of complete charge-discharge cycles is usually within 300 times).
- It has a slow charging speed.
(4) Application Scenarios:
It is mainly used in scenarios such as the starting power source for automobiles, short-distance and low-speed electric vehicles, and backup power sources with low requirements for power outage time, like solar street lamps.
Note:
- Energy density: refers to the electrical energy stored by a battery per unit volume or per unit mass and is related to the amount of electricity that can be stored under a given space or weight limitation. Common units are Wh/L and Wh/kg.
- Cycle life: refers to a complete charge – discharge process of a battery under normal use conditions as a cycle, and the number of charge – discharge cycles that a battery can withstand. A longer cycle life means that the battery can work stably for a longer period of time, reducing the frequency and cost of battery replacement.
Lithium – ion Battery
(1) Principle:
Lithium-ion batteries mainly rely on the intercalation and deintercalation of lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes to achieve the charging and discharging process, and are vividly called “rocking chair batteries“.
- During charging, an external power source inputs voltage, forcing the positive electrode material to release lithium ions. These lithium ions pass through the separator and reach the interlayer structure of the graphite on the negative electrode to complete the intercalation.
- During discharging, the lithium ions in the graphite of the negative electrode are extracted and migrate to the positive electrode through the electrolyte and are intercalated into the positive electrode material. The movement of lithium ions generates an electric current.
(2) Advantages:
- They have a high energy density and are lightweight.
- They have a long service life of four to five years, and the number of complete charge-discharge cycles can exceed 500 times.
- They have a high charging and discharging efficiency.
(3) Disadvantages:
- They have a relatively high cost.
- They have relatively strict requirements for the usage environment.
(4) Classification:
According to common positive electrode materials, they can be divided into lithium iron phosphate batteries and ternary lithium batteries (including lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide (NMC) batteries and lithium nickel cobalt aluminum (NCA) batteries). Among them, lithium iron phosphate batteries are resistant to high temperatures, while ternary lithium batteries are resistant to low temperatures.
(5) Application Scenarios:
They are applied to portable electronic devices with high requirements for energy density and portability, long-endurance and high-performance electric vehicles, and efficient energy storage systems, such as portable power stations.
Note:
Charging – Discharging Efficiency: It refers to the ratio of the output energy (discharging) to the input energy (charging) during the battery’s charging and discharging processes. It reflects the degree to which the battery effectively utilizes energy during the energy – conversion process.
What we Have for Solar Energy Storage Batteries


①: Lead – acid Battery
②: LiFePO4 Battery (Transparent Shell)
③: Flexible Stacking LiFePO4 Battery Brick
④: Rack Mounted Lithium Energy Storage Battery
⑤: Wall mounted lithium energy storage battery
⑥: Movable LiFePO4 Home energy storage
You may also be interested in pages below
- Alibaba – Gidita Life
- Ecer – Gidita Solar
- Amoy Brand – Gidita Solar
- Gidita Solar
- Solar System & Application FAQs
- Distinction Between Off-Grid, On-Grid, and Hybrid Solar System? No More Confusion, all in 1 Basic Article!
- The 4 Most Popular Solar Lights
- What is a solar lighting system? 6 Things You Need to Know About the Exciting Green Energy Lighting Solution!
- Why Balcony Solar Systems Become Booming All the World? Your Balcony can be a 100% Powerful Energy Hub!
- A Portable Power Station: Your Reliable Companion to On-the-Go Life Adventures! Learn All about A Portable Power Station in 1 article.
- From traditional refrigerators to solar refrigerators, what exactly has changed?
- The Magical Box of Energy Conversion: Solar Inverter! Everything You Want to Know is in 1 article!
- Do you know solar panel well? 2 articles let you fully understand everything about solar panel! (1)
- Do you know solar panel well? 2 articles let you fully understand everything about solar panel! (2)
- Mini Pond Pump, an Amazing Solar Solution for Water Gardening!


Xiamen Geno Industry Co,. Ltd.
Tel / WhatsApp: +86 13906057667
Email: cathy@geno-china.com