To begin with
In the current era of pursuing sustainable energy, solar power generation systems have become a hot topic. Want to buy but don’t know which system to choose? After reading this article, you will immediately know what kind of system suits you, and even what accessories you should buy! Let’s take an in-depth look at off-grid solar systems, on-grid solar systems, and hybrid solar systems.
On-grid Solar System
I) What is the on-grid solar system?
An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied solar system, is when solar panels are put in and connected to the main power grid. Extra electricity made by the panels is sent to the grid when you don’t need it all. When the solar power isn’t enough, you get power from the grid. It usually doesn’t need battery storage and depends on the grid for a balance.
II) What does an on-grid solar system consist of?
- solar panel
- micro inverter
- accessories (eg. screws, cables, brackets, etc.)
III) How does an on-grid system work?


IV) What are the applications of on-grid solar system?
- For urban residences, like the balcony solar system
- For business purposes, such as shopping malls and office buildings
- For industrial facilities
V) What is an example of an on-grid system?
- Balcony Micro Grid-connected Tied System
- Foldable Balcony Solar System with Micro Inverter
- Hanging Balcony Solar System with Micro Inverter
VI) How much does an on-grid solar system cost?
The price of the most popular on-grid solar systems, ranging from 600w to 800w, varies from $320 to $380, specifically:
You can obtain further quotations by contacting us.
VII) Component of on-grid solar system:
1) Solar Panel
1. How many solar panels do I need to run on-grid?
2. How much solar power do I need to run the on-grid solar system?
Most governments require a maximum power of 800w. Power greater than this needs to be approved. Therefore, the power options of an on-grid solar system ranging from 600W to 800W are the most popular. They typically require 2 solar panels of 450W each.
You can obtain tailored combinations and quantities of solar panels by contacting us.
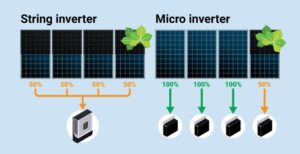
2) Micro On-grid Inverter
1. What is the function of micro on-grid inverters?


4. How to connect a micro inverter to an on-grid solar system?
Off-grid Solar System
I) What is the off-grid solar system?
An off-grid system is an independent solar power generation and can store that power in batteries. It does not connect to the power grid.
II) What does an off-grid solar system consist of?
- solar panel
- controller
- battery
- inverter (in some cases)
- accessories (eg. screws, cables, brackets, etc.)
III) How does an off-grid system work?
The working principle of an off-grid system is that:
- Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
- This DC power then passes through a charge controller, which regulates the charging process and protects the batteries from overcharging.
- The batteries store the electricity for later use.
- When there is an electricity demand, the stored DC power is sent to an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power various electrical appliances and devices.


IV) What are the applications of off-grid solar system?
- For camping and outdoor adventures
- For farms and agricultural buildings in isolated areas
- For facilities in remote regions, such as communication towers or remote research stations in deserts, mountains that have no access to the main grid, etc.
V) What is an example of an off-grid system?
VI) How much does an off-grid solar system cost?
GIDITA Solar provides you with the lowest factory-direct price.
The price of the most popular off-grid solar systems, ranging from 3kw to 8kw, varies from $2,000 to $5,000, specifically:
You can obtain further quotations by contacting us.
VII) Component of off-grid solar system:
1) Solar Panel
Same as in the on-grid system, the size of the solar panel affects the power. When sold, brackets and wires are provided for matching.
1. How many solar panels do I need to run off-grid?
It depends on the amount of power you require. Generally, each solar panel represents 560w.
The power options of an off-grid solar system ranging from 3kw to 8kw are the most popular. They typically need 5 to 14 pieces of solar panels, specifically:
You can obtain tailored combinations and quantities of solar panels by contacting us.
2. How much solar power do I need to run the off-grid solar system?
It depends on your electric power consumption.
- If the average daily electricity consumption of your household is 10 – 20 kWh, it may be appropriate to choose a 3 – 5 kW off-grid solar system.
- If the electricity consumption is 20 – 30 kWh, a 5 – 8 kW off-grid solar system may be more suitable.
This is only a rough reference. You can consult our professionals to determine.
2) Solar Controller
1. What is the function of controller?
2. How to choose between PWM controllers and MPPT controllers?
- PWM controllers are cost-effective and work by modulating the pulse width.


- MPPT controllers can track the maximum power point of the solar panel in real-time to ensure maximum energy output from the solar panel. Therefore, they are usually more efficient, can provide faster and more stable charging. At the same time, MPPT can accept a wider range of input voltages and convert them efficiently to voltages suitable for battery charging. However, due to more complex technology, the cost is usually higher.


Therefore, if the efficiency and performance requirements of the solar power generation system are high, especially in unstable lighting conditions or when it is desired to make more full use of the energy of the solar panel, the MPPT controller is a better choice; if the budget is limited and the performance requirements of the system are not particularly demanding, the PWM controller can also meet the basic needs.
3. In which situation should we use Built-in Frequency converters?
For example, in some equipment with higher requirements for rotational speed and power control, such as solar air conditioners with frequency conversion compressors, controllers with frequency converters can precisely adjust the rotational speed of the compressor according to the supply of solar energy, thereby achieving more energy-saving and stable operation.
4. How to connect a controller to an on-grid solar system?

3) Battery
The battery is used to store the electricity generated by solar energy for power supply when the sunlight is weak or absent.
4) Off-grid Inverter
1. What is the function of off-grid inverters?
2. How to choose between VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) and inverters?
- Inverters only convert DC power into AC power with a fixed frequency and voltage but do not change the frequency. They are usually used in some devices with low requirements for changes in power frequency and voltage, such as converting the DC power generated by solar panels into the commonly used 220V, 50Hz AC power in households to supply power to general household appliances.




3. How to connect a inverter to an off-grid solar system?
Hybrid Solar System
I) What is the hybrid solar system?
There are 2 types of hybrid solar systems:
- The first type can handle both off-grid and on-grid operations simultaneously. The output interface can be connected to sell any extra energy to the grid.
- The second type is an off-grid solar system combined with an energy source from the grid. However, the output interface of this type cannot be connected to sell any extra energy to the grid.
Most of the products available in the market are of the second type.
II) What does a hybrid solar system consist of?
- solar panel
- hybrid inverter (with built-in controller and inverter)
- battery
- accessories (eg. screws, cables, brackets, etc.)
III) How does a hybrid system work?


IV) What are the applications of hybrid solar system?
- Home energy storage systems
- Small commercial places
- Some scenarios with high requirements for power supply reliability and energy utilization efficiency
V) What is an example of a hybrid system?
VI) How much does a hybrid solar system cost?
GIDITA Solar provides you with the lowest factory-direct price.
The price of the most popular hybrid solar systems, ranging from 5kw to 10kw, varies from $3,900 to $7,200, specifically:
- 5kw: $3,900
- 8kw: $6,500
- 10kw: $7,200
You can obtain further quotations by contacting us.
VII) Component of hybrid solar system:
1) Solar Panel
1. How many solar panels do I need to run hybrid?
It depends on the amount of power you require. Generally, each solar panel represents 560w.
The power options of a hybrid solar system ranging from 5kw to 10kw are the most popular. They typically need 10 to 20 pieces of solar panels, specifically:
- 5kw: 10 pieces
- 8kw: 16 pieces
- 10kw: 20 pieces
You can obtain tailored combinations and quantities of solar panels by contacting us.
2. How much solar power do I need to run the hybrid solar system?
It depends on your electric power consumption.
- If the average daily electricity consumption of your household is 20 – 30 kWh, it may be appropriate to choose a 5 – 8 kW hybrid solar system.
- If the electricity consumption is 30 – 40 kWh, an 8 – 10 kW hybrid solar system may be more suitable.
This is only a rough reference. You can consult our professionals to determine.
2) Hybrid Inverter
1.What is the function of hybrid inverters?
The hybrid inverter is an electrical conversion device that can handle both off-grid and on-grid functions:
- During off-grid operation, when the power grid is down, the hybrid inverter uses the power from the battery or solar panels to supply power to each loads, achieving independent power supply.
- During on-grid operation, when the power grid is normal, it can feed back the excess solar power to the power grid, achieving “self-consumption with surplus power sold to the grid”, saving electricity costs and generating revenue.
2. How to connect a hybrid inverter to a hybrid solar system?
Summary
I) Which is better, on-grid or off-grid solar system?
- On-grid solar systems are usually a more cost-effective choice, as they allow you to save money on your electricity bill and potentially earn credits. They also don’t require expensive battery banks like off-grid systems do.
- Off-grid solar systems offer independence from the power grid, which can be beneficial in remote areas or during power outages.
II) Which is better, hybrid or off-grid solar system?
- Off-grid solar systems are ideal if you are in a location with no access to the main power grid. It provides power solely based on the solar panels and any attached battery storage. However, it often requires a significant investment in batteries and may have limitations in providing continuous high-power output.
- Hybrid solar systems are suitable for those who have a reliable grid connection and want to balance costs, as they combine the benefits of solar power with the option to draw from the grid or other backup sources when needed. You don’t need as large of a battery storage capacity compared to a pure off-grid system.
You may also be interested in pages below
- Alibaba – Gidita Life
- Ecer – Gidita Solar
- Amoy Brand – Gidita Solar
- Gidita Solar
- Solar System & Application FAQs
- Distinction Between Off-Grid, On-Grid, and Hybrid Solar System? No More Confusion, all in 1 Basic Article!
- 6 Types of Solar Water Pumps Systems – Powerful Irrigation And Water Supply?
- Are Solar Air Conditioner Any Good? Revolutionary Energy-Saving More than 99% Air Conditioning System
- Why Balcony Solar Systems Become Booming All the World? Your Balcony can be a 100% Powerful Energy Hub!


Xiamen Geno Industry Co,. Ltd.
Tel / WhatsApp: +86 13906057667
Email: cathy@geno-china.com